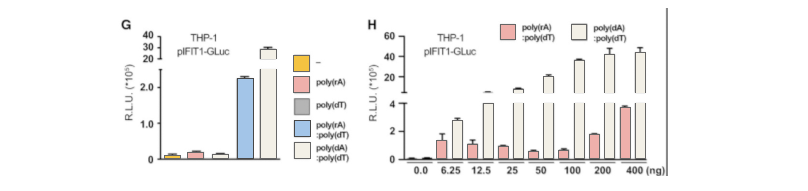
RNAi technology used to be popular in biological research, especially in high-throughput genetic screening, gene function study, clinical treatments for antivirus and cancers. However, the RNAi technology has been questioned because of its off-target effect. In recent years, the emerging CRISPR gene editing technology is widely used in almost every biological field. Because of its high specificity, low off-target effect and wide application prospects, CRISPR is replacing RNAi as the best choice for most research.
What RNAi might cost you?
One of the biggest limitations of the RNAi silencing method is that it suffers from High off-target effects. RNAi might silence unintended RNA targets resulting in modified phenotypes and therefore influence gene function screening experiments. There are three reasons for this high off-target effect:
· siRNA may compete with the intrinsic microRNA in RISC complex, resulting in affecting the function of microRNA and the expression regulation of other genes;
· siRNA also targeted sequences with limited complementarity;
· siRNA may interact with the 3'UTR of unintended RNA, leading to its degradation.
Other than high-off target effect, issues researchers are facing with are that:
· shRNA fails to show any reduction in protein expression level;
· No suppression but overexpression of target genes;
· Transcripts with high turnover are difficult to silence;
· Non-coding sequences are difficult to silence.
· siRNA may compete with the intrinsic microRNA in RISC complex, resulting in affecting the function of microRNA and the expression regulation of other genes;
· siRNA also targeted sequences with limited complementarity;
· siRNA may interact with the 3'UTR of unintended RNA, leading to its degradation.
Other than high-off target effect, issues researchers are facing with are that:
· shRNA fails to show any reduction in protein expression level;
· No suppression but overexpression of target genes;
· Transcripts with high turnover are difficult to silence;
· Non-coding sequences are difficult to silence.
CRISPR has replaced RNAi as the best choice for most research applications:
Researchers conducted parallel experiments with shRNA libraries and CRISPR gRNA libraries, which proved that the efficiency and reliability of using gRNA libraries to screen genes was much higher than that of shRNA libraries.
In addition to high efficiency and high true positive rate, the off-target effect of CRISPR is very low. Because its specificity depends on two aspects, one is the base pairing between gRNA and target DNA, the other is that the Cas9-gRNA complex only binds to the PAM sequence in the genome. Only when these two conditions are met at the same time can Cas9 cause DSB.
Although RNAi was adopted as a gene silencing technique first, CRISPR has surpassed RNAi in popularity due to several advantages made possible by advancements that have refined CRISPR technology. The main reason for the popularity of CRISPR is it's specific yet versatile nature. At the same time, the choice remains with the user to perform knockouts, knock-ins, or knockdown experiments, making CRISPR extremely versatile.
In addition to high efficiency and high true positive rate, the off-target effect of CRISPR is very low. Because its specificity depends on two aspects, one is the base pairing between gRNA and target DNA, the other is that the Cas9-gRNA complex only binds to the PAM sequence in the genome. Only when these two conditions are met at the same time can Cas9 cause DSB.
Although RNAi was adopted as a gene silencing technique first, CRISPR has surpassed RNAi in popularity due to several advantages made possible by advancements that have refined CRISPR technology. The main reason for the popularity of CRISPR is it's specific yet versatile nature. At the same time, the choice remains with the user to perform knockouts, knock-ins, or knockdown experiments, making CRISPR extremely versatile.
Combine RNAi with CRISPR technology:
· Combined shRNA over CRISPR/cas9 as a methodology to detect of-target efects and a potential compensatory mechanism
· CRISPR knockout screening outperforms shRNA and CRISPRi in identifying essential genes
· Systematic comparison of CRISPR/Cas9 and RNAi screens for essential genes
· Choosing the Right Tool for the Job: RNAi, TALEN, or CRISPR
https://www.ubigene.us/about/news/523.html